Stability and reproducibility of solid electrolyte amperometry sensors at the analysis of hydrogen in nitrogen-containing gas mixtures
Abstract
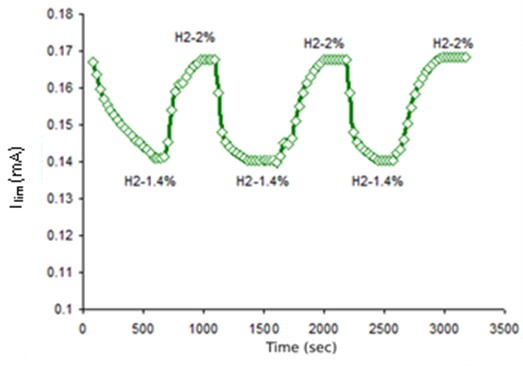
This paper illustrates the results of long-term tests on the stability of the output signal of the solid electrolyte amperometry sensor when measuring the hydrogen concentration in the H2 + N2 gaseous mixture. The obtained experimental data verify the stability and reproducibility of the sensor output signal for hydrogen concentration measurements in the nitrogen-containing gaseous mixture during > 8000 h of operation. The output signal drift, i.e., the limiting current value, was insignificant, less than ± 5 %. The sensor operation was performed at 3 temperature shifts with different time intervals; these changes did not have any impact either on the sensor integrity or on its operation. The structure of the solid electrolyte sensor, intermediate solid electrolyte / electrode layer and electrodes did not undergo any significant changes during operation. The dynamic characteristics of the sensor, the response time in particular, remained stable during the operation.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Okamoto H, Obayashi H, Kudo T, Carbon monoxide gas sensor made of stabilized zirconia, Solid State Ion., 1(3–4) (1980) 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(80)90012-0
Zheng Y, Wang J, Yu B, Zhang W, et al., A review of high temperature co-electrolysis of H2O and CO2 to produce sustainable fuels using solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs): advanced materials and technology, Chem. Soc. Rev., 46 (2017) 1427–1463. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00403B
Fadeev GI, Kalyakin AS, Somov SI, Electrode potentials of electrochemical cells with oxide-conducting solid electrolyte in chemically nonequilibrium gas mixtures, Russ. J. Electrochem., 45 (2009) 429–433. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193509040119
Volkov A, Neimin A, Sosnovsky V, Study of durability of the solid electrolyte electrochemical sensors with etalon electrodes of the Me-MexOy type at measuring of the oxygen concentration of the gaseous media (Issledovaniye dolgovechnosti tverdoelektrolitnykh electrokhimicheskikh datchikov s etalonnymi electrodami tipa Me-MexOy pri izmerenii kislorodsoderzhaniya gazovykh sred), Zavodskaya laboratoriya, 48 (1982) 6–8.
Zhuiykov S, Miura N. Solid-state electrochemical gas sensors for emission control. In book: Sorrell CC, Sugihara S, Nowotny J (eds) Materials for energy conversion devices. Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge; 2005. 303–335 pp. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845690915.2.303
Park CO, Fergus JW, Miura N, Park J, Choi A, Solid-state electrochemical gas sensors, Ionics, 15 (2009) 261–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-008-0300-6
Kalyakin A, Demin A, Gorbova E, Volkov A, Tsiakaras A, Sensor Based on a Solid Oxide Electrolyte for Measuring the Water Vapor and Hydrogen Content in Air, Catalysts, 12(12) (2022) 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121558
Shuk P, Bailey E, Guth U, Zirconia Oxygen Sensor for the Process Application: State-of-the-Art, Sens. Transducers, 90 (2008) 174–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-008-0274-4
Liu T, Jin H, Li L, Yu J, A novel method for preparing dense diffusion barrier limiting current oxygen sensor, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 101(4) (2018) 1537–1543. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.15302
Sekhar PK, Brosha EL, Mukundan R, Nelson MA, et al., Development and testing of a miniaturized hydrogen safety sensor prototype, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 148(2) (2010) 469–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.05.031
Flege E, Vonau C, Guth U, Characterization of Pt,O2|YSZ electrodes for lambda probes and their ageing in humid atmosphere, Technisches Messen, 84(10) (2017) 635–643. https://doi.org/10.1515/teme-2016-0079
Lalauze R, Visconte E, Montanaro L, Pijolat C, A new type of mixed potential sensor using a thick film of beta alumina, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 13(1–3) (1993) 241–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(93)85371-G
Guillet N, Lalauze R, Pijolat C, Oxygen and carbon monoxide role on the electrical response of a non-Nernstian potentiometric gas sensor; proposition of a model, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 98(2–3) (2004) 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2003.10.001
Driesner O, Gumprecht F, Guth U, In situ measurements of O2 and CO eq. in cement kilns, J. Sens. Sens. Syst., 6(2) (2017) 327–330. https://doi.org/10.5194/jsss-6-327-2017
Chevallier L, Di Bartolomeo E, Grilli ML, Mainas M, et al., Non-Nernstian planar sensors based on YSZ with a Nb2O5 electrode, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 129(2) (2008) 591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2007.09.037
Park CO, Akbar SA, Weppner W, Ceramic electrolytes and electrochemical sensors, J. Mater. Sci., 38 (2003) 4639–4660. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027454414224
Katahiraa K, Matsumotoa H, Iwaharaa H, Koidea K, Iwamoto T, A solid electrolyte hydrogen sensor with an electrochemically-supplied hydrogen standard, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 73(2–3) (2001) 130–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00672-9
Xia ChY, Lu XCh, Yan Y, Wang T, et al., Improved performances of oxygen potentiometric sensor by electrochemical activation, J. Solid State Electrochem., 16 (2012) 2523–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1556-8
Pasierb P, Rekas M, Solid-state potentiometric gas sensors–current status and future trends, J. Solid State Electrochem., 13 (2009) 3–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0556-9
Möbius H-H, Hartung R, Solid-state potentiometric gas sensors–a supplement, J. Solid State Electrochem., 14 (2010) 669–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-009-0839-9
Pasierb P, Rekas M, Solid-state potentiometric gas sensors–current status and future trends, J. Solid State Electrochem., 13 (2009) 3–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0556-9
Maskell WC, Steele BCH, Solid state potentiometric oxygen gas sensors, J. Appl. Electrochemistry, 16 (1984) 475–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01006843
Iwahara H, Uchida H, Ogaki K, Nagato H, Nernstian hydrogen sensor using BaCeO3-based, proton-conducting ceramics operative at 200–900 °C, Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 138 (1991) 295–299. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2085558
Chao Y, Yao S, Buttner WJ, Stetter JR, Amperometric sensor for selective and stable hydrogen measurement, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 106(2) (2005) 784–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.09.042
Lu X, Wu S, Wang L, Su Z, Solid-state amperometric hydrogen sensor based on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 107(2) (2005) 812–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.12.022
Tan Y, Tan TC, Sensing behaviour of an amperometric hydrogen sensor, J. Electrochem. Soc., 142 (1995) 1923–1928. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2044215
Sakthivel M, Weppner W, A portable limiting current solid-state electrochemical diffusion hole type hydrogen sensor device for biomass fuel reactors: engineering aspect, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 33(2) (2008) 905–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2007.10.048
Kalyakin AS, Volkov AN, Meshcherskikh AN, Dunyushkina LA, Dual chamber YSZ‑based sensor for simultaneous measurement of methane and water vapor concentrations in CH4 + H2O + N2 gas mixtures, J. Solid State Electrochem., 26 (2022) 739–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05116-y
Medvedev D. Kalyakin A, Volkov A, Demin A, Tsiakaras P, Electrochemical moisture analysis by combining oxygen- and proton-conducting ceramic electrolytes, Electrochem. commun., 76 (2017) 55–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2017.01.003
Taniguchi N, Kuroha T, Nishimura C, Iijima K, Characteristics of novel BaZr0.4Ce0.4In0.2O3 proton conducting ceramics and their application to hydrogen sensors, Solid State Ion., 176(39–40) (2005) 2979–2983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2005.09.035
Kalyakin AS, Medvedev DA Volkov AN, Electrochemical zirconia-based sensor for measuring hydrogen diffusion in inert gases, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 169 (2022) 057530. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac725d
Bao J, Okuyama Y, Shi Z, Ohno H, et al., Properties of Electrical Conductivity in Y- Doped CaZrO3. Mater. Trans., 53 (2012) 973–979. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.m2012017
Goppel W, Reinhardt G, Rasch M, Trends in development of solid state ampermetric and potentiometric high temperature sensors, Solid State Ion, 136(1–2) (2000) 519–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00410-0
Kalyakin AS, Volkov AN, Meshcherskikh AN, Dunyushkina LA, Dual chamber YSZ based sensor for simultaneous measurement of methane and water vapor concentrations in CH4 + H2O+ N2 gas mixtures, Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 26 (2022) 739–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05116-y
Somov SI, Reinhardt G, Guth U, Göpel W, Tubular amperometric high-temperature sensors: simultaneous determination of oxygen, nitrogen oxides and combustible components, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 65(1–3) (2000) 68–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(99)00341-X
Katahira K, Matsumoto H, Iwahara H, Koide K, Iwamoto T, A solid electrolyte steam sensor with an еlectrochemically supplied hydrogen standard using proton-conducting oxides, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 67(1–2) (2000) 189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00400-7
Uchida H, Maeda N, Iwahara H, Relation between proton and hole conduction in SrCeO3-based solid electrolytes under water-containing atmospheres, Solid State Ionics, 11(2) (1983) 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(83)90048-6
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/elmattech.2024.3.026
Copyright (c) 2024 Anatoly S. Kalyakin, Aleksander N. Volkov, Maxim Yu. Gorshkov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

