(Y0.82La0.18)3Fe5O12–x: structure and transport properties
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Heraeus WC. Uber die elektrolytische Leitung Fester Korper bei sehr hohen. Temperaturen, Elektrochem., 6(2) (1899) 41–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbpc.18990060205
Ishihara T, Matsuda H, Takita Y, Doped LaGaO3 Perovskite Type Oxide as a New Oxide Ionic Conductor, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 116 (1994) 3801–3803. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00088a016
Feng M, Goodenough JB, A superior oxide-ion electrolyte, European Journal of Solid State and Inorganic Chemistry, 31 (1994) 663–672. https://doi.org/10.1002/CHIN.199507014
Liu H, Yuan L, Wang S, Fang H, et al., Structure, optical spectroscopy properties and thermochromism of Sm3Fe5O12 garnets, J. Mater. Chem. C, 4 (2016) 10529–10537. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc02830f
Yamagishi T, Awaka J, Kawashima Y, Uemura M, et al., Ferrimagnetic order in the mixed garnet (Y1-xGdx)3Fe5O12, Philos. Mag., 85(17) (2005–2006), 1819–1833. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500830500038092
Phan MH, Morales MB, Chinnasamy CN, Latha B, et al., Magnetocaloric effect in bulk and nanostructured Gd3Fe5O12 materials, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 42 (2009) 115007. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/11/115007
Al-Omari IA, Skomski R, Sellmyer DJ, Magnetic Properties of Y3-2xCa2xFe5-xVxO12 Garnets, AMPC, 2 (2012) 116–120. https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2012.23019
Jiang L, Yang Sh, Zheng M, Chen H, Wu A, Synthesis and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Gd3Fe5O12 and GdFeO3 powders prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method, Mater. Res. Bull., 104 (2018) 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.04.010
Cherepanov V, Kolokolov I, L'vov V, The saga of YIG: Spectra, thermodynamics, interaction and relaxation of magnons in a complex magnet, Phys. Rep., 229(3) (1993) 81–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/0370-1573(93)90107-O
Gomez-Perez JM, Oyanagi K, Yahiro R, Ramos R, Absence of evidence of spin transport through amorphous Y3Fe5O12, Appl. Phys. Lett., 116(3) (2020) 032401. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5119911
Fechine PBA, Moretzsohn RST, Costa RCS, Derov J, et al., Magneto-dielectric properties of the Y3Fe5O12 and gd3fe5o12 dielectric ferrite resonator antennas, ASB Microw. Opt., 50(11) (2008) 2852–2857. https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.23824
Guo X, Rak Zs, Tavakoli AH, Becker U, et al., Thermodynamics of thorium substitution in yttrium iron garnet: comparison of experimental and theoretical results, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2 (2014) 16945–16954. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta03683b
Guo X, Rak Zs, Tavakoli AH, Sutton S, et al., Cerium Substitution in Yttrium Iron Garnet: Valence State, Structure, and Energetics, Chem. Mater., 26(2) (2014) 1133–1143. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm403444f
Guo X, Kukkadapu RK, Lanzirotti A, Newville M, et al., Charge-Coupled Substituted Garnets (Y3−xCa0.5xM0.5x)Fe5O12 (M = Ce, Th): Structure and Stability as Crystalline Nuclear Waste Forms, Inorg. Chem., 54(8) (2015) 4156–4166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b00444
Guo X, Navrotsky A, Kukkadapu RK, Engelhard MH, et al., Structure and thermodynamics of uranium-containing iron garnets, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 189 (2016) 269–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.043
Long GJ, Grandjean F, Guo X, Navrotsky A, et al., Mossbauer Spectral Properties of Yttrium Iron Garnet, Y3Fe5O12, and Its Isovalent and Nonisovalent Yttrium-Substituted Solid Solutions, Inorg. Chem., 55(7) (2016) 3413–3418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b02769
Navrotsky A, Lee W, Mielewczyk-Gryn A, Ushakov SV, et al., Thermodynamics of Solid Phases Containing Rare Earth Oxides, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 88 (2015) 126–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2015.04.008
Becker S, Ren Z, Fuhrmann F, Ross A, et al., Magnetic Coupling in Y3Fe5O12/Gd3Fe5O12 Heterostructures, Phys. Rev. Applied, 16 (2021) 014047. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.16.014047
Mullerbuschbaum H, Vonpostel M, Eine weitere Oxovanadat-Phase mit Granatstruktur: Ca5Mg3ZnV6O2, Allg. Chem., 615(9) (1992) 101–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19926150920
Baettig P, Oguchi T, Why Are Garnets Not Ferroelectric? A Theoretical Investigation of Y3Fe5O12, Chem. Mater., 20 (2008) 7545–7550 https://doi.org/10.1021/cm801786h
Shkerin SN, Tolkacheva AS, Mayenite (A Review), Russian Journal of General Chemistry, 92(11) (2022) 2312–2333. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363222110160
Larsen PK, Metselaar R, Defects and the Electronic Properties of Y3Fe5O12, J. Solid State Chem., 12(3–4) (1975) 254–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(75)90315-1
KJacob KT, Rajitha G, Nonstoichiometry, defects and thermodynamic properties of YFeO3, YFe2O4 and Y3Fe5O12, Solid State Ion., 224 (2012) 32–40 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2012.07.003
Huang S, Shi LR, Sun HG, Li CL, et al., High temperature dielectric response in Sm3Fe5O12 ceramics, J. Alloys Compd., 674 (2016) 341–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.001
Kharton VV, Shaula AL, Naumovich EN, Vyshatko NP, et al., Ionic Transport in Gd3Fe5O12- and Y3Fe5O12-Based Garnets, J. Electrochem. Soc., 150(7) (2003) J33–J42. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1574810
Waerenborgh JC, Rojas DP, Shaula AL, Kharton VV, et al., Defect formation in Gd3Fe5O12-based garnets: a Mfssbauer spectroscopy study, Mater Lett., 58 (2004) 3432–3436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.05.081
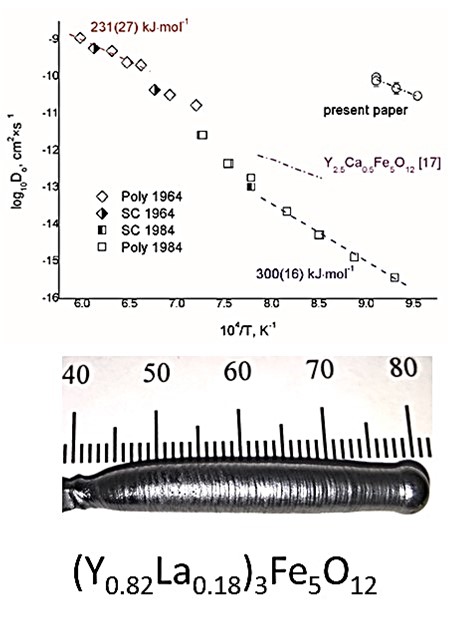
Paladino AE, Maguire EA, Rubin LG, Oxygen Ion Diffusion in Single-Crystal and PoIycrystaIIine Yttrium Iron Garnet, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 47(6) (1964) 280–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1964.tb14416.x
Kilner JA, Steele BCH, Ilkov L, Oxygen self-diffusion studies using negative-ion secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), Solid State Ion., 12 (1984) 89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(84)90134-6
Shkerin SN, Ulyanova ES, Naumov SV, Shmakov AN, et al., The interaction of defects in a mayenite structure, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 22 (2020) 27818–27828. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp05107a
Tolkacheva AS, Shkerin SN, Porotnikova NM, Kuznetsov MV, et al., Oxygen surface exchange and diffusion in mayenite single crystal, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 21 (2019) 24740–24748. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP04936C
Bhosale DR, Yusuf SM, Kumar A, Mukadam MD, et al., High oxide ion conductivity below 500 °C in the garnets
LaxY3-xFe5O12+δ, Phys. Rev. Mater., 1 (2017) 015001. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.1.015001
Yousaf M, Akhtar MN, Yousaf Shah MAK, Rauf S, et al., Evaluation of rare earth (Yb, La) doped (Sm3Fe5O12) garnet ferrite membrane for LT-SOFC, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy., 46 (2021) 9996–10006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.166
Gyrdasova OI, Stepanov AE, Naumov SV, Shkerin SN, The influence of synthesis conditions on the formation of the Y3-xLaxFe5-yO12+δ/La1-xYxFe1-yO3 composite, Physical and chemical aspects of the study of clusters, nanostructures and nanomaterials, 14 (2022) 583–592. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.26456/pcascnn/2022.14.583
Gyrdasova OI, Pasechnik LA, Krasilnikov VN, Surikov VT, Kuznetsov MV, Sorption and photocatalytic activity of
Zn1-xCuxO (x = 0.05 and 0.15) to As(III) in alkaline medium, Physical and chemical aspects of the study of clusters, nanostructures and nanomaterials, 12 (2020) 792–804. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.26456/pcascnn/2020.12.792
Ezin AN, Tsidilkovski VI, Kurumchin EKh, Isotopic exchange and diffusion of oxygen in oxides with different bulk and subsurface diffusivities, Solid State Ion., 84(1–2) (1996) 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(96)83012-8
Klier K, Kučera E, Theory of exchange reactions between fluids and solids with tracer diffusion in the solid, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 27(6–7) (1966) 1087–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(66)90084-9
Mizusaki J, Mima Y, Yamauchi S, Fueki K, et al., Nonstoichiometry of the perovskite-type oxides La1−xSrxCoO3−δ, Solid State Chem., 80(1) (1989) 102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(89)90036-4
Ananyev MV, Tropin ES, Eremin VA, Farlenkov AS, et al., Oxygen isotope exchange in La2NiO4±d, Phys. Chem. Chem Phys., 18 (2016) 9102–9111. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP05984D
Lyubutin IS, Gavriliuk AG, Trojan IA, Sadykov RA, Magnetic Collapse in Yttrium Iron Garnet Y3Fe5O12 at High Pressure, Jetp. Lett., 82 (2005) 702–707. https://doi.org/10.1134/1.2171723
Rotman S, Tuller H, Defect-Property Correlations in Garnet Crystals. *VII: The Electrical Conductivity and Defect Structure of Yttrium Aluminum and Yttrium Iron Garnet Solid Solutions, J. Electroceram., 2 (1998) 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009974923893
Yaremchenko AA, Kharton VV, Viskup AP, Naumovich EN, et al., Oxygen Ionic and Electronic Transport in LaGa12xNixO32d Perovskites, J. Solid State Chem., 142(2) (1999) 325–335. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1998.8041
Elshof JE, Lankhorst MHR, Bouwmeester HJM, Oxygen Exchange and Diffusion Coefficients of Strontium-Doped Lanthanum Ferrites by Electrical Conductivily Relaxation, J. Electrochem Soc., 144(3) (1997) 1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837531
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/elmattech.2024.3.046
Copyright (c) 2024 Sergey N. Shkerin, Anna S. Tolkacheva, Sergey V. Naumov, Olga I. Gyrdasova, Anton E. Stepanov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

